Don't you hate it when you just want to start a tutorial, but you discover you need that pesky database to get going?
Well, worry no more, because I'll give you the easiest way to create a database from scratch and start working.
Make sure you have docker installed and then run this command in the terminal
docker run --name myNewMySqlDockerContainer -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=mySecretRootPassword -e MYSQL_USER=myUserName -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=mySecretPassword -e MYSQL_DATABASE=myDbName -v D:/Projects/Database:/var/lib/mysql -p 3306:3306 -d mysql:latest
If you want to know more about what just happened, read below.
The docker run command will do the following:
create a docker container called
myNewMySqlDockerContainerevery time it sees
-eit sets an environment variable in that image so:- it sets an environment variable called
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDwith the valuemySecretRootPassword - it sets an environment variable called
MYSQL_USERwith the valuemyUserName - it sets an environment variable called
MYSQL_PASSWORDwith the valuemySecretPassword - it sets an environment variable called
MYSQL_DATABASEwith the valuemyDbName- (These environment variables are what your mysql will need in order to know the root password for the user called
root, if the database has another user, and in our case it has, what is the password for that user and what is the actual database name. They are also the values you will use in your framework to connect to the database.)
- (These environment variables are what your mysql will need in order to know the root password for the user called
- it sets an environment variable called
when it sees
-vit will bind mount avolume. In translation, it will make sure that the data that should go in the mysql folder of the container (/var/lib/mysql- this is the default path of mysql in every mysql docker container), actually goes in the folder on your machine (in my case:D:/Projects/Database)when it sees
-pit will bind theporton your machine to the port on the container so this way, you can connect from your machine to the mysql that is in the docker containermyMachinePort:containerPort
when it sees
-dit will run the container in the background and print the container IDwhen it sees
mysql:latestit will know to download thelatestversion ofmysqlin the container
How to see your new database
- download MySQL Workbench and open it
- create a new connection (the little + sign next to connections)
- add the data you just created with docker (notice the port and user name) (for the password, click on 'Store in Keychain')
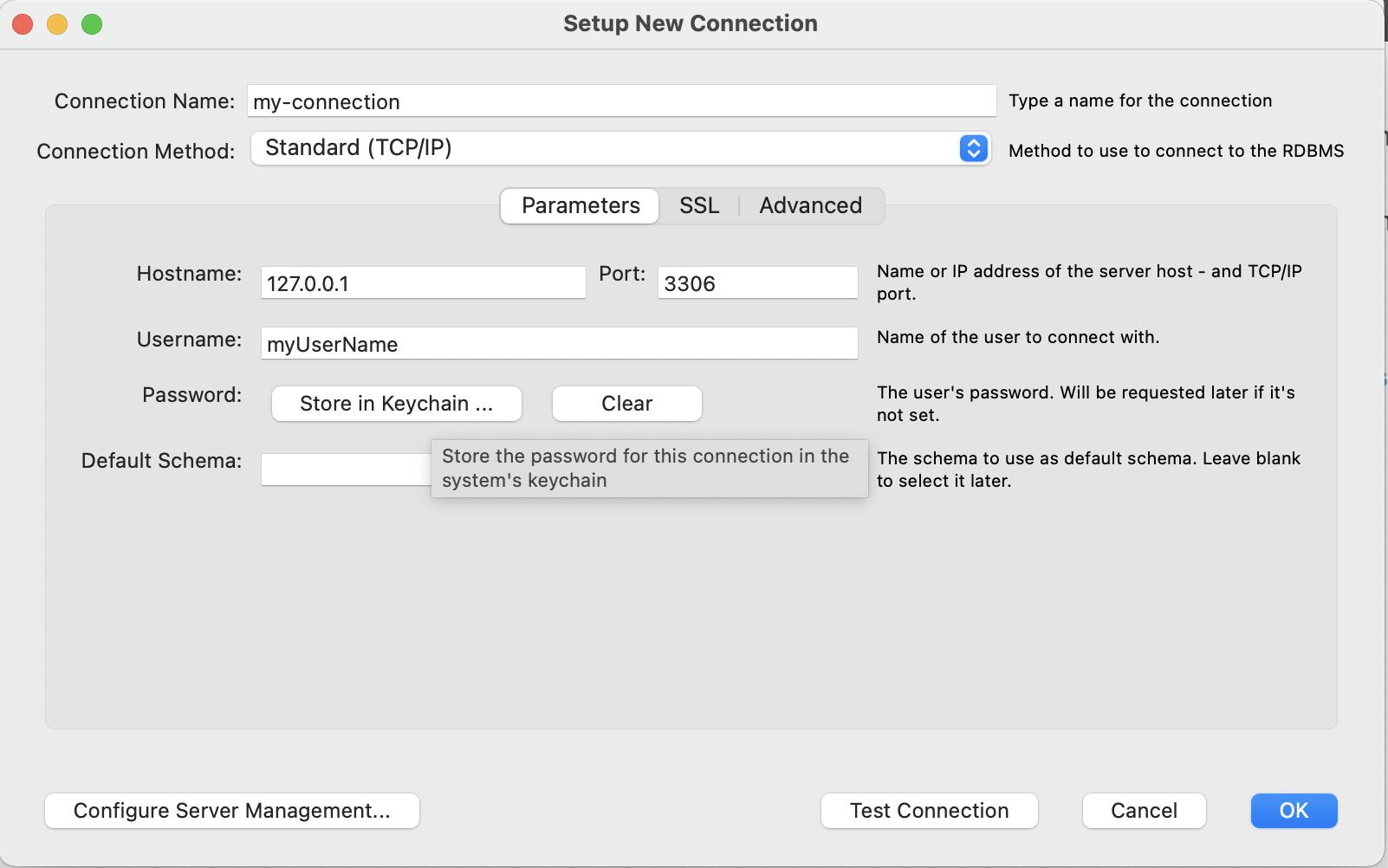
Note: you can use also the username: root with the password mySecretRootPassword that you created above
That's about it. I hope it helps some of you, for a quick and easy mysql database creation to enjoy your tutorials. For more docker flags, check out this .

